- Home
- Wear and Tear of the Hip Joint – Osteoarthritis of the Hip
Wear and Tear of the Hip Joint – Osteoarthritis of the Hip
What is it? How does Osteoarthritis of the Hip develop?
A healthy joint is covered by cartilage. The contact surfaces in the joint have a smooth coating which hardly causes any friction during movement. If this joint cartilage is used up for mechanical reasons, the condition is referred to as osteoarthritis. The used up cartilage exposes the bones, and eventually there is bone-to-bone contact within the joint. This leads to sterile inflammation, which irritates the synovial membrane (synovia) and stimulates the production of synovial fluid. This in turn stretches the joint capsule, which is extremely sensitive to pain.
The most common causes of Osteoarthritis
- Number 1: Impingement syndrome of the hip This can occur in younger adults. If this is not recognised and treated in time, the cartilage can become worn and movements, starting up and walking can become painful. This is the cause for about 50% – 60% of all patients who require early joint replacement surgery. Impingement
- Primary hip osteoarthritis (cause not yet known for certain)
- Death of the femoral head (femoral head necrosis)
- Childhood hip diseases, maldevelopment (hip dysplasia Perthes disease)
Symptoms of Hip Osteoarthritis
Hip pain due to wear and tear
- Start-up pain with morning stiffness. The hip joint feels “rusty” in the morning when taking the first steps.
- The walking distance is limited due to the pain, the patient has to sit down.
- Putting on socks, shoes, walking upstairs can be painful in the groin.
- The mobility of the hip is limited.
- Night-time hip pain can occur.
Treatment at Praxis Leonardo
Without Surgery – Conservative
Very often specific physiotherapy is useful to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint. The mechanics of walking, the movements can thus be optimized and the pain reduced. Patients with good musculature have a faster recovery (prehabilitation) even in the event of a later possible operation.
Injection Therapy (Infiltration) locally into the Joint. There are several options:
1) Anti-inflammatory (cortisone) – effective for night pain with inflammatory component. Effective for about 3-4 months.
2) Hyaluronic acid infiltration to lubricate the joint – if the joint space is still visible on the x-ray
3) ACP / PRP- Autologous blood therapy
Surgical Treatment – Hip Joint Replacement
If the conservative measures fail and there is persistent suffering, then hip joint replacement is recommended.
Before an operation, digital planning is carried out to record and measure your individual anatomy. This allows the exact positioning of the replacement joint during the operation to be planned very precisely in advance.
Which Hip Replacement Surgery will be used?
In our practice all joint replacement operations on the hip are performed exclusively via the minimally invasive anterior (front) approach.
Surgical access to the hip joint is made through an anatomical gap between the muscles without injuring or loosening them.
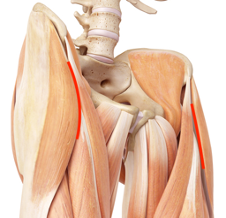
Hip replacement via anterior (front) approach
The muscles are pushed to the side, allowing access to the joint. After this operation, compared to hip operations via the posterior or external access to the hip joint, patients are able to move independently again much faster, as the muscles are not injured.
The front (anterior) access to the hip joint has significant advantages for you compared to conventional approaches.
- Your recovery to pain-free mobility is much faster. Even older patients can partly walk without crutches during their stay in hospital (5 nights).
- There is less risk of dislocation because the muscles that stabilize the joint remain intact.
What can I expect from the Operation?
Pain
The pain subsides significantly within 3-4 days. On the basis of reliable long-term data, you have a 95% chance of becoming completely pain-free after the implantation of a total hip prosthesis and practically forgetting your hip. Pain remains in about 5% of patients. These are different from those before the operation. Depending on what the cause is, it can be resolved.
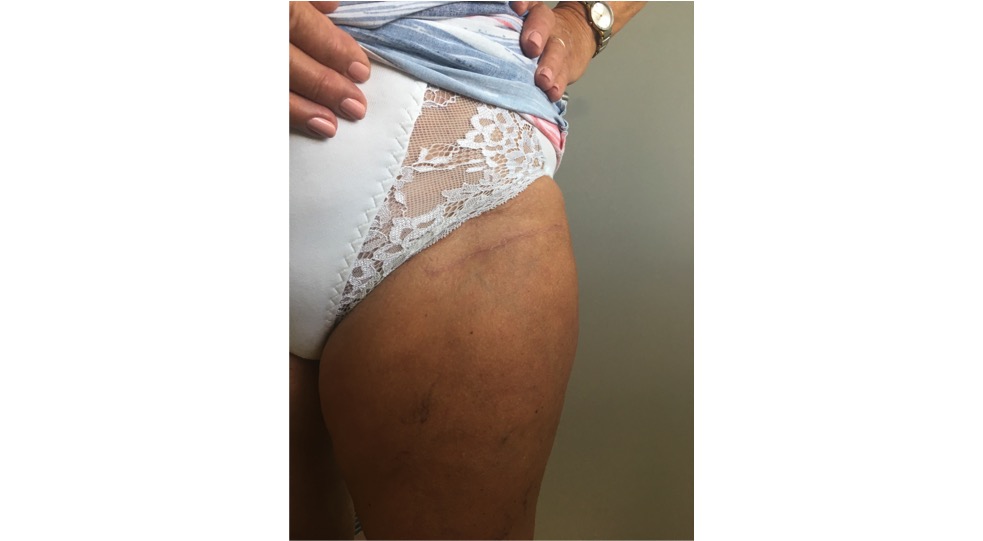
Hip joint replacement after 3 months (bikini cut)
Mobility
On the day of the operation, you may stand up in the presence of an accompanying person and put full weight on the leg. You only need the forearm crutches for stability. The point in time when you can walk without the crutches is very much dependent on the duration of previous complaints and the resulting muscle condition. At the latest after 6 weeks, you can omit the crutches. Patients with good musculature and good coordination often do without their crutches at home after a few days.
Long Term Results
With a correct surgical technique and reliable implants, patients over the age of 50 have a very high chance (85%) that they will not need another operation for 20 years. In younger patients under the age of 50, about one third (32%) will need a change of operation by the end of their life.
Risks and Complications
Dislocation (Luxation) of the Artificial Hip Joint
The frequency of a hip joint luxation varies depending on the surgical approach chosen. With the minimally invasive anterior (anterior) approach, the risk is less than 1%, compared to 1-3% with conventional approaches.
Infection
According to the literature, the frequency is between 0.5-0.7% despite maximum safety measures and antibiotic administration immediately before the operation. In such cases a detailed examination and identification of the pathogens is essential.
Thrombosis, Pulmonary Embolism
There is a risk of developing a thrombosis, i.e. blood clots in the deep veins of the legs, with any operation. For this reason, blood thinning for 6 weeks is recommended despite early mobilization.
Blood Transfusion
Only in very rare cases is a blood transfusion required after a total hip replacement.
Broken Bones
During the operation such a complication is very rare. After the operation it may happen in the event of a fall. Especially older patients are at risk of accidents. With prosthetic sockets without cement this occurs more often (3%) than with cemented sockets (0.6%). For this reason, the prosthesis socket is cemented in patients of advanced age. The durability of these prosthesis sockets is extremely satisfactory. However, they are less suitable for younger patients with sporting ambitions.
Replacement

Only proven implants with excellent long-term data are used in our practice, which individually and precisely replicate the patient’s anatomy. (cement free, just as with cemented implants)
Surface Combination
This means the combination of the materials used from the head of the hip prosthesis to the socket. Ceramic-ceramic combination (for younger active patients) and ceramic-highly cross-linked polyethylene are used, both with minimal abrasion.
Recovery – Rehabilitation
Inpatient rehabilitation is only necessary in rare cases, mainly for single patients or patients of advanced age. Outpatient physiotherapy is recommended for at least 6 weeks after the operation. The aim is to strengthen the muscles around the joint, normalise the movement pattern and restore confidence in the usual gait.
Return to Work, Everyday Life
The incapacity to work is of course dependent on your activity. As a rule, you will be unable to work for about 6 weeks. Most patients can then return to their jobs without any problems.
Sport with a total Hip Prothesis

Sport with Hip joint Replacement
- Exercise bike from day 7
- Cycling as soon as you can safely get on and off the bike (4-6 weeks)
- Skiing, tennis after 2-3 months
- Hiking after 6 weeks